Environmental Stewardship Branch
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
This collection of data summarizes the companies reporting under the Renewable Fuels Regulations. This data set includes total liquid petroleum fuel volumes, renewable fuel volumes, and compliance unit creation. This data set also includes information on compliance by company. The information was provided to Environment and Climate Change Canada under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999.
-
This collection of data summarizes the companies and facilities reporting under the Fuels Information Regulations, No. 1. This dataset includes total fuel volumes, sulphur contents and masses, and companies reporting production and/or importation of liquid fuels originating from crude oils, coal or bituminous sand. The information was provided to Environment and Climate Change Canada under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999.
-
Canada has the longest coastline in the world, measuring 243,790 kilometers. Many of our waterways along the coastline have to be dredged regularly to keep shipping channels and harbours open and safe for navigation; and this material is sometimes best disposed of at sea. Schedule 5 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (CEPA) defines an exclusive list of materials and substances suitable for disposal at sea in Canada, which is in accordance with the London Protocol (1996). They are: dredged material, fish waste resulting from industrial fish processing operations, ships or platforms, inert and inorganic geological matter, uncontaminated organic matter of natural origin, and bulky substances. The disposal of any substance into the sea, on the seabed, in the subsoil of the seabed, or onto ice, from a ship, an aircraft, a platform or other structure is not allowed unless a permit is issued by the Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) Disposal at Sea Program. Incineration at sea, as well as importing or exporting a substance for disposal at sea is also prohibited. More information on Disposal at Sea is available at: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/disposal-at-sea.html The Active and Inactive Disposal at Sea Sites in Canadian Waters dataset provides spatial and related information of at-sea disposal sites approved for use in Canada in the last ten years and that remain open for consideration for additional use. Any additional use of a disposal site must be conducted in accordance with the terms and conditions of a valid Disposal at Sea permit. The dataset may be of use in relation to Disposal at Sea permit applications. For some Disposal at Sea permit applications the data may be of use in assessing serious harm to fish under the Fisheries Act and assessing interference with navigation under the Navigation Protection Act.
-
Sidney Island Shorebirds Survey peep counts.
-
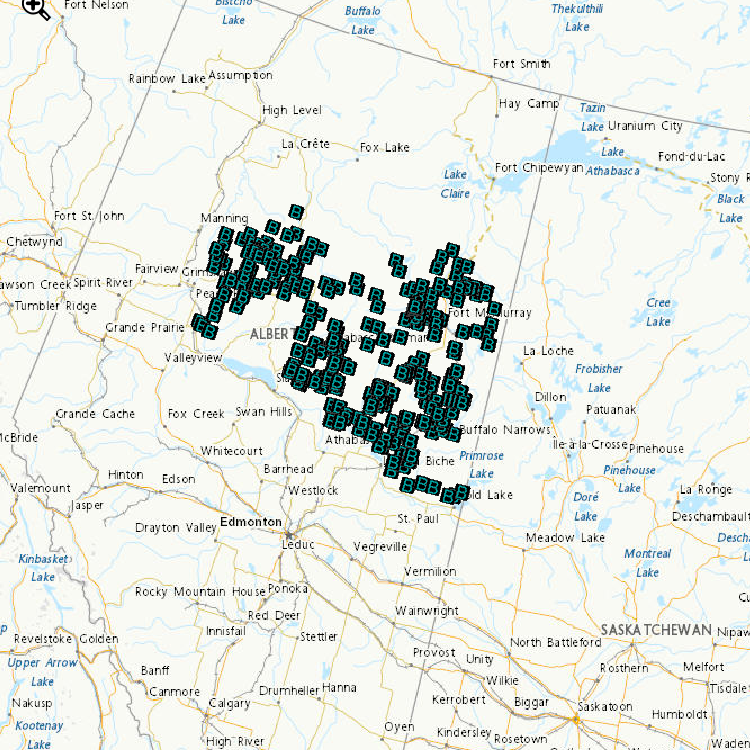
Environment and Climate Change Canada’s cause-effect monitoring is focused on understanding how boreal songbirds, including several Species at Risk, are affected by human activity in the oil sands area, particularly the impact of the physical disturbance of forested habitats from exploration, development and construction of oil sands. Determining the abundance of songbird species associated with various habitat type(s) and understanding how the type and number of birds varies with type and amount of habitat, are important components of assessing the effect of habitat disturbance. Regional-scale monitoring focuses on understanding how and why boreal songbirds, including several Species at Risk, are affected by human activity across the Peace, Athabasca and Cold Lake oil sands area. Local-scale projects focus on addressing gaps in our understanding of complex response patterns at regional scales by targeting specific habitats or development features of interest. These data contribute to: a. improving the design of monitoring programs; b. explaining observed trends in populations (why bird populations are increasing or decreasing); c. predicting population sizes within the oil sands area; and d. assessing the individual, additive and cumulative effects of oil sands and other resource development on boreal birds. Data are used by ECCC and our partners to develop new models and increase the robustness of existing models of bird responses to habitat and disturbance. Because models can be used to predict outcomes of future land management scenarios, these models can assist decision-making by helping evaluate land-use choices before impacts are directly observed.
-
Survey areas is a polygon feature class containing mudflats and staging areas observed for shorebirds.
-
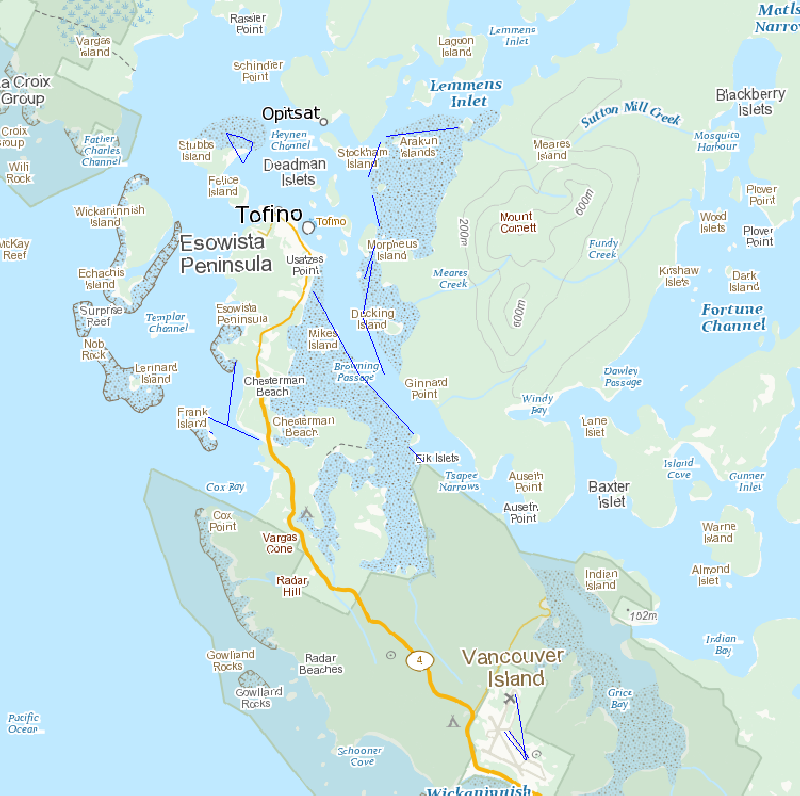
Survey transects is a line feature class containing transects completed in 2011.
-
Surveyor shorebird bird observations and counts for all years.
-
Survey points is a point feature class containing transects and observations completed in 2011.
-
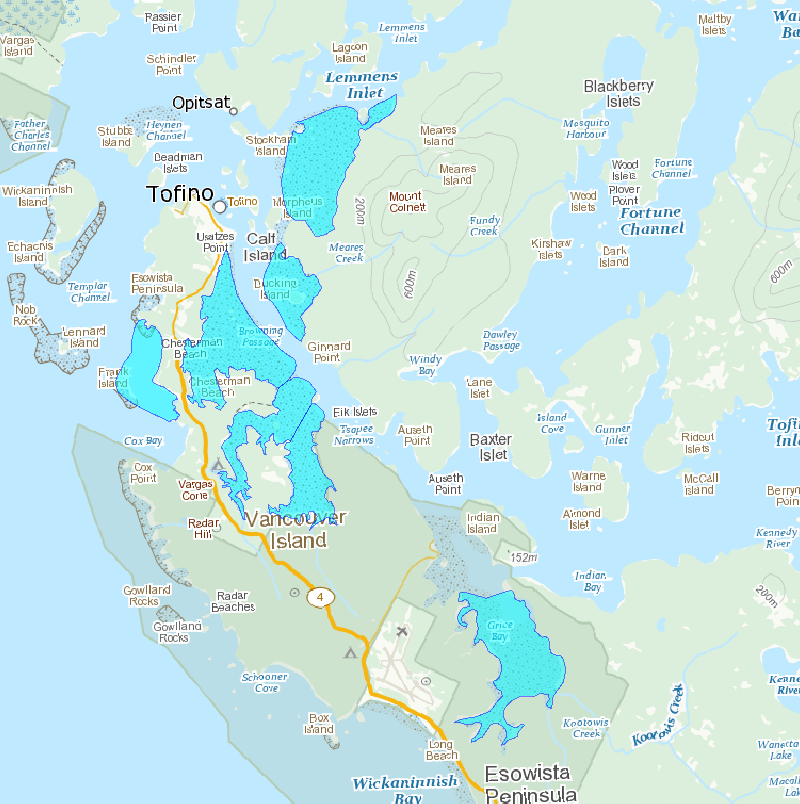
The surveys are conducted along the sandspit and within a 96 ha lagoon that encompasses mudflats, eelgrass beds, and saltmarsh at the northwest end of Sidney Island, located in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia. The survey counts numerate two species, Western Sandpiper (Calidris mauri) and Least Sandpiper (Calidris minutilla), during a portion of the southern migration period (July, August, and early September), and have been conducted intermittently since 1990. Sidney Island (48°37’39’N, 123°19’30”W) is located within the Salish Sea (Strait of Georgia), 4 km off the coast of Vancouver Island in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Southbound Western and Least Sandpipers stop over within Sidney Spit Marine Park (part of the Gulf Islands National Park Reserve), roosting and feeding along the sandspit and within a 96 ha lagoon that encompasses mudflats, eelgrass beds, and saltmarsh at the northwest end of the island. These species are the most numerous shorebird species using the area during southern migration. Adults precede juveniles, arriving at the end of June and throughout July. Juveniles reach the site in early August, with their numbers trailing off in early September. As a result, the site experiences a transition from purely adult to purely juvenile flocks over the course of the season. Daily counts, beginning in early July and ending in early September, were conducted in 1990 and from 1992-2001 (no counts occurred in 1991). Effort was reduced to weekly surveys between 2002 and 2013. Over the entire monitoring period median survey effort was 9 counts annually. All counts were conducted at the low tide of the day, when shorebirds were feeding in the exposed mudflat of the lagoon. Observers walked along the shore of the lagoon stopping periodically at vantage points to look for birds. For ease of data recording and to keep track of individual flocks, the survey area was divided into separate units demarcated by prominent geographical features. Counts were made with the unaided eye, through binoculars, and with a 20 – 60x zoom spotting scope, depending on the proximity of the birds. All individuals in small flocks were counted and individuals in large flocks were estimated by counting in groups of 5, 10, 50 or 100 according to flock size in each successive field of view across a scan of the entire flock. Between 1990 and 2001, when daily counts were conducted, birds were occasionally counted more than once in a day. The largest count value obtained was used as the daily estimate for these days. For smaller flocks, we were able to identify all individual birds to species and age-class. Sub-samples from larger flocks were also aged (adult or juvenile) and identified to species. Birds were aged by plumage characteristics. Adult Western Sandpipers are distinguished from juveniles by the dark chevron markings present along the sides and breast. Juvenile Least Sandpipers have a buffy breast compared to the distinct, darker one of the adult, and juveniles have bright rufous scapulars compared to the drab feather-edges of the adults. In both species, juvenile plumage appears brighter and cleaner than adult plumage, which is more worn and tattered.
